SiC MOSFET (650V-1700V):Epi (Drift+Buffer) Layer Survey Report
Overview
In SiC devices, in addition to determining the maximum operating and breakdown voltages, the structure and engineering of the SiC Epitaxial layer contains a significant amount of know-how to mitigate the adverse effects of crystal defects in the surface-active layer of vertical transistors. Since SiC substrates are not yet standardized, almost every SiC device manufacturer prepares the Epi layer with its own recipe, and the structure of each Epi layer is different (see P.3).
◆ Based on the data we have collected (SEM, SCM, etc.), this survey report presents:
1) Types of Epi layer/Buffer layer structures used by major manufacturers
2) Details of Epi layers for patent certification
3) Comprehensive academic and industrial references overview
4) Impact of Epi layers on manufacturing costs
Product features
Report contents and Summary of results (42 pages)
The table of contents and excerpts from this report are listed on the following pages.
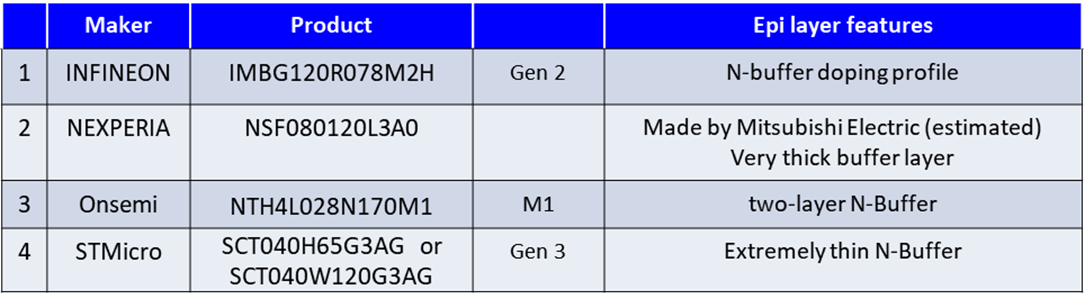
- Extraction and comparison of N-Buffer structures for preventing BPD (Basal Plane Dislocation) from major SiC manufacturers.
- The thickness of the N-Buffer layer varies greatly depending on the manufacturer, ranging from 0.4 μm to over 10 μm.
- The carrier concentration of each layer is extracted by SEM and SCM analysis, and the doping of the N-Buffer layer is 1E17 to 1.5E18 at/cm3.
- The cost of the Epi layer is estimated to be as much as 120% of the cost of a raw SiC substrate wafer (150 mmΦ) for a thick Epi layer.
- A “screening” test is considered necessary to supplement the N-Buffer layer.
Report price
Delivered one week after order placement
Please contact us for report pricing.









